Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to treat abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) and, less commonly, thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAA). An aneurysm is a dangerous bulging or ballooning in the wall of an artery, and when it occurs in the aorta, the body’s main blood vessel, it can be life-threatening if it ruptures.
EVAR allows surgeons to repair the aneurysm by reinforcing the weakened section of the aorta without the need for traditional open surgery. This procedure is a major advancement in vascular surgery, providing a less invasive alternative to open surgical repair with faster recovery times and lower risks.
What is an Aortic Aneurysm?
An aortic aneurysm occurs when the wall of the aorta weakens, causing it to enlarge. If left untreated, the aneurysm can grow and eventually rupture, leading to severe internal bleeding and, often, death. Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) occur in the lower section of the aorta, while thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) occur in the chest area.
Risk factors for aneurysms include:
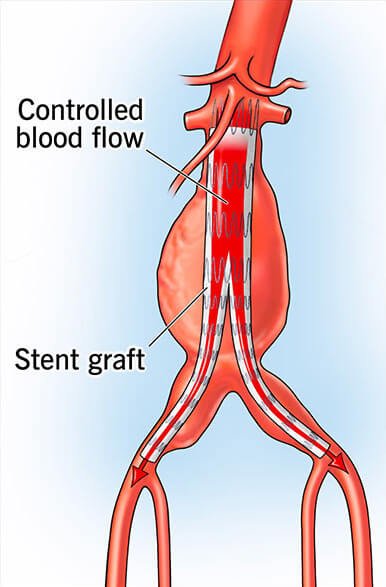
The EVAR Procedure: How it Works
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) involves placing a stent graft inside the aorta at the location of the aneurysm. The stent graft acts as a scaffold, reinforcing the weakened aorta and preventing the aneurysm from growing or rupturing. Here's how the procedure is generally performed:
Benefits of EVAR
Despite its advantages, EVAR is not without risks, and it may not be suitable for all patients. Some potential challenges include: