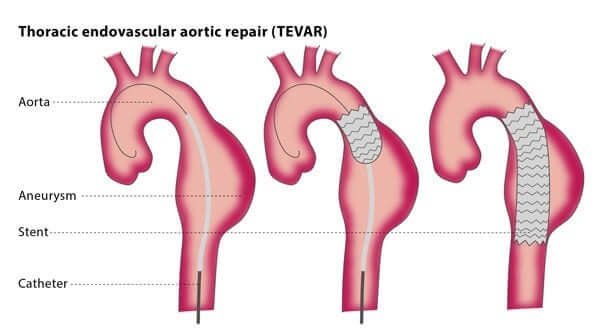
Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR)
Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat aortic disease in the thoracic (chest) region of the body. The primary purpose of TEVAR is to repair the aorta, the largest artery in the body, in cases where it has been damaged or weakened, such as in the presence of an aortic aneurysm, dissection, or trauma.
What is TEVAR?
TEVAR involves the insertion of a stent graft into the damaged portion of the thoracic aorta. A stent graft is a fabric-covered metal mesh tube that reinforces the weakened section of the artery, allowing blood to flow properly and preventing the aneurysm from rupturing. Unlike traditional open surgery, where a large incision is made, TEVAR uses a catheter-based approach, making it a less invasive option for patients.
Conditions Treated with TEVAR
TEVAR is used to treat several serious conditions affecting the thoracic aorta, including:
The TEVAR Procedure
Benefits of TEVAR
Risks and Considerations
While TEVAR has many advantages, there are also some risks involved, including:
Who is a Candidate for TEVAR?
TEVAR is often recommended for patients who are considered at high risk for traditional open surgery due to age, overall health, or the complexity of their aortic condition. However, not every patient with aortic disease is a candidate for TEVAR. Factors such as the size and location of the aneurysm, the patient’s anatomy, and other medical conditions will be taken into account when deciding if TEVAR is the best treatment option.