Left Atrial Appendage (LAA) Closure
Left Atrial Appendage (LAA) Closure is a minimally invasive procedure designed to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), particularly those who cannot tolerate long-term anticoagulation therapy. Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm that significantly increases the risk of blood clots forming in the left atrial appendage (LAA), a small, pouch-like structure in the left atrium of the heart. These clots can break loose and travel to the brain, causing a stroke.
The LAA closure procedure involves sealing off the appendage to prevent blood clots from forming and entering the bloodstream.
Why LAA Closure is Necessary?
For patients with AFib, the irregular beating of the atria (upper chambers of the heart) can cause blood to pool and clot in the LAA. Most strokes in AFib patients originate from blood clots formed in the LAA. To prevent these clots from traveling to the brain, many AFib patients are prescribed blood thinners like warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). However, some patients cannot take these medications due to bleeding risks or other complications, making LAA closure a vital alternative.
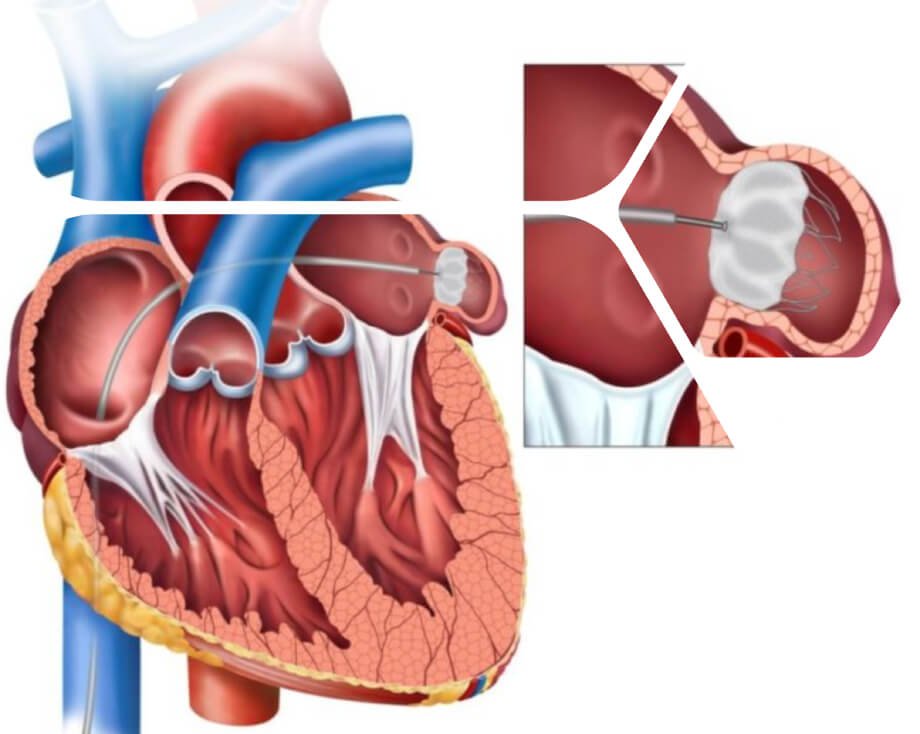
The LAA Closure Procedure
The most commonly used device for LAA closure is the WATCHMAN device, though others like the Amplatzer Amulet are also used. The procedure involves:
Benefits of LAA Closure
Who is a Candidate for LAA Closure?
Not all patients with AFib are suitable candidates for LAA closure. It is generally recommended for patients who:
Physicians will perform a detailed evaluation, often using imaging studies, to determine if the patient’s anatomy and health status make them a suitable candidate for LAA closure.
Outcomes and Long-Term Success
Studies have shown that LAA closure with devices like the WATCHMAN can be as effective as anticoagulation therapy in reducing stroke risk, particularly in patients who cannot take blood thinners. Long-term follow-up is necessary to monitor for device-related complications or residual leaks.
The success of the procedure has led to growing adoption worldwide, providing patients with a viable alternative to blood thinners. As technologies evolve, newer devices and techniques are being developed to further improve the safety and efficacy of LAA closure.
Risks and Considerations
Like all medical procedures, LAA closure comes with some risks, including: